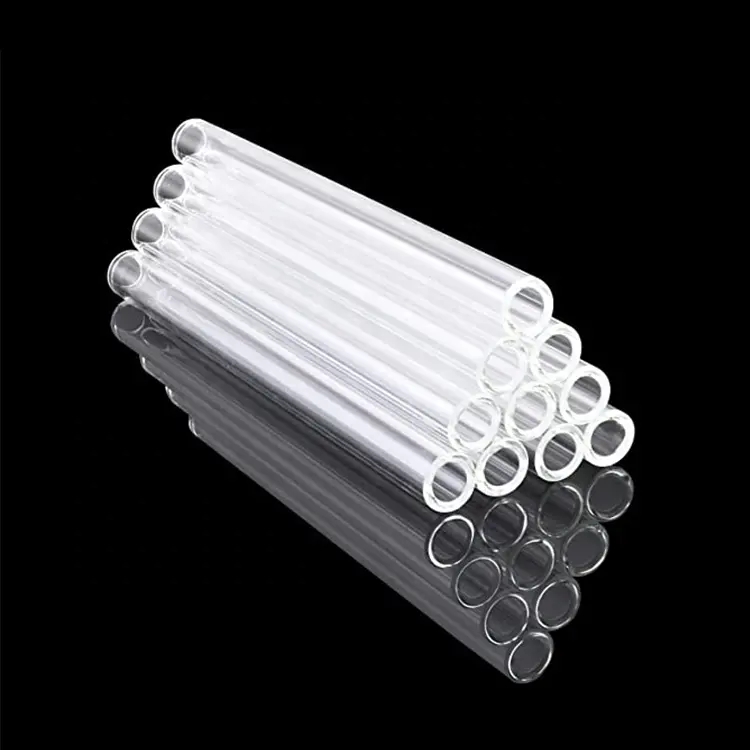
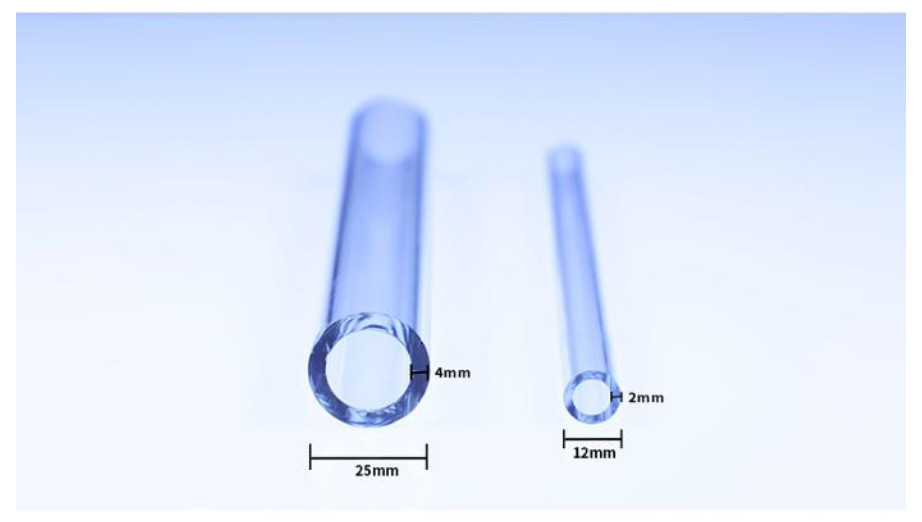
Borosilicate Tubing: Exploring Its Many Facets
Introduction:
Borosilicate tubing, a versatile and exceptional material, has carved out a significant niche in various industries, from scientific research to industrial manufacturing. In this comprehensive article, we will embark on a journey through the world of borosilicate tubing, examining its composition, properties, manufacturing processes, and diverse applications.
Section 1: The Essence of Borosilicate Tubing
Borosilicate tubing is a unique type of glass, characterized by its high boron oxide content. The fusion of boron and silica in its composition imparts borosilicate glass with extraordinary qualities, including outstanding thermal resistance, exceptional chemical resilience, and remarkable transparency. Its low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) makes it an ideal choice for applications exposed to rapid temperature fluctuations.
Section 2: Unlocking the Attributes of Borosilicate Tubing
High Thermal Resistance: Borosilicate tubing is engineered to endure extreme temperature fluctuations, rendering it indispensable for applications subject to high heat, such as laboratory glassware and industrial furnaces.
Exceptional Chemical Durability: Its robust chemical resistance makes borosilicate glass the material of choice for storing and transporting sensitive substances, including pharmaceuticals and chemicals, ensuring their safety and stability.
Low CTE: The low coefficient of thermal expansion minimizes the risk of cracking or shattering during abrupt temperature changes, guaranteeing the durability and reliability of the glass.
Superior Transparency: Recognized for its exceptional optical clarity, borosilicate glass is widely used for high-quality optical components, camera lenses, and artistic glasswork, including intricate glass sculptures.
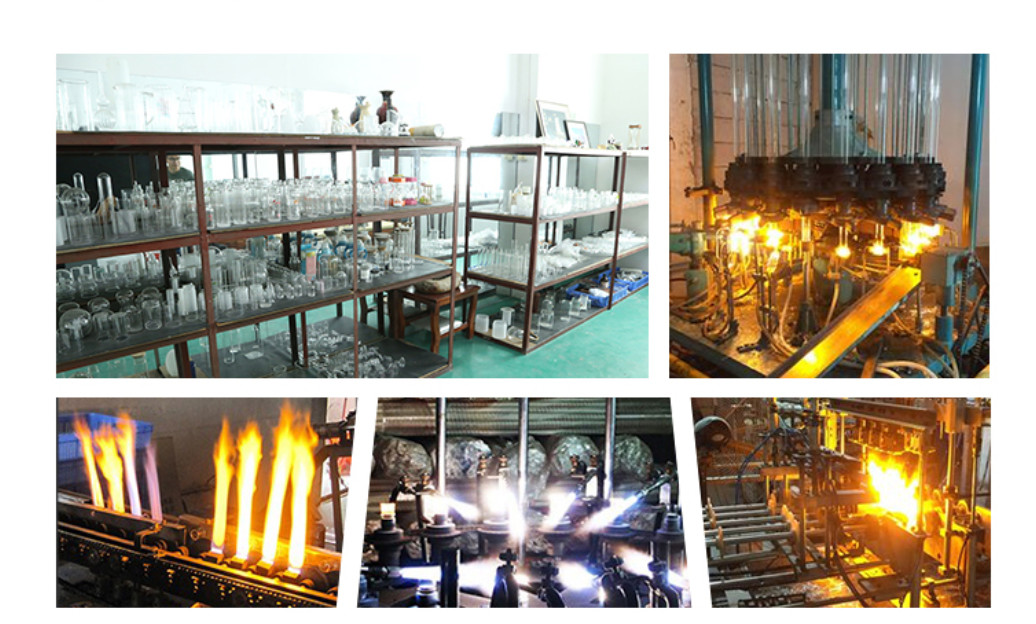
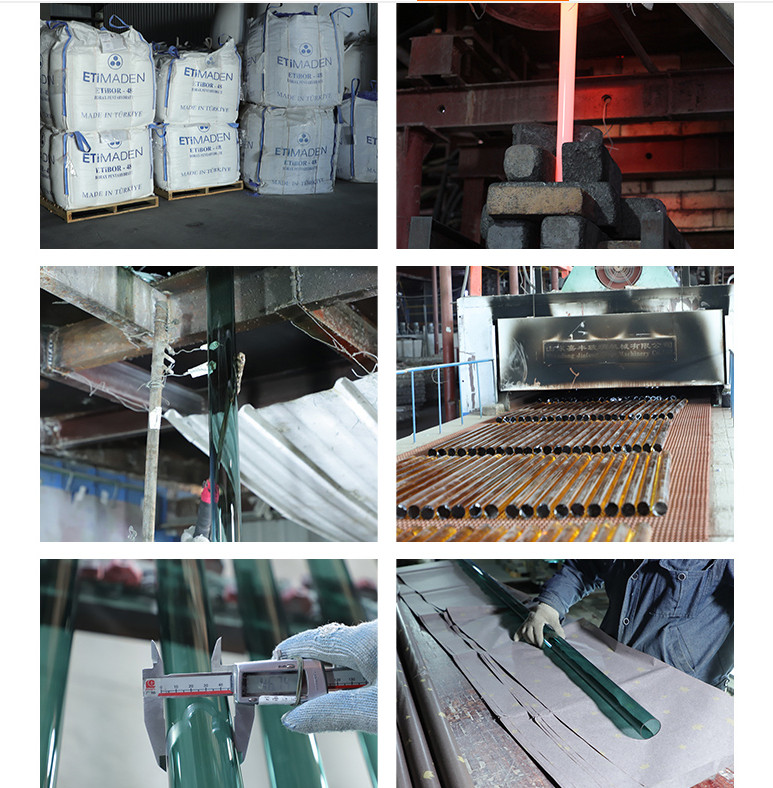
Section 3: Crafting Borosilicate Tubing
The manufacturing of borosilicate tubing is a meticulous process, involving the precise melting and blending of high-purity silica and boron oxide. The resulting mixture is expertly shaped into tubes using methods such as the Danner process and the Vello process. Subsequently, gradual cooling relieves internal stresses, enhancing the glass’s strength and resilience. It can then be tailored to meet specific requirements through cutting, polishing, and shaping.
Section 4: Varied Applications of Borosilicate Tubing
Laboratory Glassware: Borosilicate tubing is the cornerstone of laboratory glassware production, used in the creation of essential items like beakers, test tubes, and pipettes, owing to its chemical resistance and optical clarity.
Pharmaceutical Packaging: In the pharmaceutical industry, borosilicate glass vials and containers are relied upon to safely store delicate medications and chemicals, ensuring product stability and safety.
Lighting and Optics: The glass’s exceptional optical properties make it a preferred choice for high-quality optical lenses, camera lenses, and artistic glasswork, including intricately designed sculptures.
Industrial Utility: Borosilicate tubing serves a vital role in various industrial processes, including semiconductor manufacturing, chemical processing, and oil refineries, due to its ability to withstand extreme temperatures and harsh chemicals.
Conclusion:
Borosilicate tubing is a remarkable material with a multitude of applications. Its unique properties, such as high thermal resistance, exceptional chemical durability, and transparency, establish it as a fundamental component across diverse industries. Whether you are a scientist, artist, or industrial engineer, borosilicate tubing is likely to be a crucial element in your work. A comprehensive understanding of its composition, properties, and manufacturing processes is vital for harnessing the full potential of this versatile material.